脱钩点 seperation point
第1题:
下面程序的输出结果是( )。 #include <iostream> using namespace std; class point { public: point(int px=10,int py=10){ x=px;y=py;} getpx( ) { return x;} getpy( ) { return y;} private: int x,y; }; void main(voiD) { point p,q(15,15); cout<<"p点的坐标是:"<<p. getpx( )<<" ,"; cout<<p. getpy( )<<endl; cout<<"q点的坐标是:"<<q. getpx( )<<" ,"; cout<<q. getpy( ); }
A.p点的坐标是:10,10 q点的坐标是:15,15
B.p点的坐标是:0,0 q点的坐标是:15,15
C.p点的坐标是:0,0 q点的坐标是:0,0
D.p点的坐标是:10,10 q点的坐标是:10,10
第2题:
A、判断(judgement)
B、决定(decision)
C、评论(criticism)
D、危机(Crisis)
E、区分(seperation)
第3题:
Shutdown price(or point,or rule) 停业价格(或停业点、停业原则)
在厂商理论中,市场价格恰恰可以弥补平均可变成本且无多余的点就是停业点。这时,企业每期的损失恰好等于它的固定成本,与停业关门的后果一样。
第4题:
涂装术语-汉译英:烘干();粗密封Rough sealing;脏点Dirty point;缩孔()。
第5题:
新安装或大修后的立井罐笼防坠器,必须进行( ),合格后方可使用。
A 不脱钩试验
B 脱钩试验
C 不脱钩和脱钩试验
第6题:
阅读以下说明和C代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在的对应栏内。
【说明】
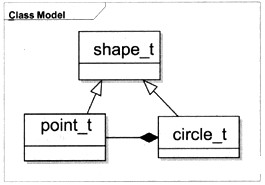
在一个简化的绘图程序中,支持的图形种类有点(point)和圆(circle),在设计过程中采用面向对象思想,认为所有的点和圆都是一种图形(shape),并定义了类型shape t、 point t和circle t分别表示基本图形、点和圆,并且点和圆具有基本图形的所有特征。
【C代码】
typedef enum { point,circle } shape type; /* 程序中的两种图形:点和圆 */
typedef struct { /* 基本的图形类型 */
shape_type type; /* 图形中类标识:点或者圆*/
void (*destroy) (); /* 销毁图形操作的函数指针*/
void (*draw) (); /* 绘制图形操作的函数指针*/
} shape_t;
typedef struct { shape_t common; int x; iht y; } point_t; /* 定义点类
型, x, y为点坐标*/
void destroyPoint (point_t* this) { free (this); printf ("Point destoryed!
\n"); } ) /* 销毁点对象*/
void drawPoint(point_t* this) { printf("P(%d,%d)", this->x, this->y); }
/* 绘制点对象*/
shape_t* createPoint (va_list* ap) (/* 创建点对象,并设置其属性*/
point_t* p_point;
if ( (p_point= (point_t*)malloc (sizeof (point_t)) ) ==NULL) returnNULL;
p_point->common, type = point; p_point->common, destroy = destroyPoint;
p_point->common.draw = drawPoint;
p_point->x = va_arg(*ap, int); /* 设置点的横坐标*/
p_point->y = va_arg(*ap, int); /* 设置点的纵坐标*/
return (shape_t*)p_ooint; /*返回点对象指针*/
}
typedef struct { /*定义圆类型*/
shape_t common;
point_t 4center; /*圆心点*/
int radius; /*圆半径*/
} circle_t;
void destroyCircle(circle_t* this){
free((1)); free(this); printf("Circle destoryed!\n");
}
void drawCircle(circle_t* this) {
print f ("C (");
(2).draw(this->center); /*绘制圆心*/
printf(",%d) ", this->radius);
}
shape_t* createCircle(va_list4 ap) { /*创建一个圆,并设置其属性*/
circle_t4 p circle;
if ((p_circle = (circle_t4)malloc (sizeof (circle_t)) ) ==NULL ) return NULL;
p_circle->common.type = circle; p_circle->common.destroy = destroy
Circle;
p_circle->common.draw = drawCircle;
(3) = createPoint(ap); /* 设置圆心*/
p_circle->radius = va_arg(*ap, int); /* 设置圆半径*/
return p_circle;
}
shape_t* createShape(shape_type st, "') { /* 创建某一种具体的图形*/
va_list ap; /*可变参数列表*/
&nbs
第7题:
A.Smooth Point(平滑曲线点)
B.Corner Point(角点)
C.Compounded Point(复合式控制点)
D.Vector Point(向量式控制点)
第8题:
Zero-profit-point 零利润点
对一个厂商而言,收支相抵时的价格水平。即全部成本得到弥补但利润为零的价格水平。
第9题:
驼峰解体车列时,车组开始脱离车列的地点称为()。
第10题:
TPS系统中Regulatory PV Point常规PV处理点的功能是什么?