(ii) Advise Andrew of the tax implications arising from the disposal of the 7% Government Stock, clearly
identifying the tax year in which any liability will arise and how it will be paid. (3 marks)
第1题:
(c) Assuming that Stuart:
(i) purchased 201,000 shares in Omega plc on 3 December 2005; and
(ii) dies on 20 December 2007,
calculate the potential inheritance tax (IHT) liability which would arise if Rebecca were to die on 1 March
2008, and no further tax planning measures were taken.
Assume that all asset values remain unchanged and that the current rates of inheritance tax continue to
apply. (6 marks)

第2题:
(c) Advise Alan on the proposed disposal of the shares in Mobile Ltd. Your answer should include calculations
of the potential capital gain, and explain any options available to Alan to reduce this tax liability. (7 marks)

However, an exemption from corporation tax exists for any gain arising when a trading company (or member of a trading
group) sells the whole or any part of a substantial shareholding in another trading company.
A substantial shareholding is one where the investing company holds 10% of the ordinary share capital and is beneficially
entitled to at least 10% of the
(i) profits available for distribution to equity holders and
(ii) assets of the company available for distribution to equity holders on a winding up.
In meeting the 10% test, shares owned by a chargeable gains group may be amalgamated. The 10% test must have been
met for a continuous 12 month period during the 2 years preceding the disposal.
The companies making the disposals must have been trading companies (or members of a trading group) throughout the
12 month period, as well as at the date of disposal. In addition, they must also be trading companies (or members of a trading
group) immediately after the disposal.
The exemption is given automatically, and acts to deny losses as well as eliminate gains.
While Alantech Ltd has owned its holding in Mobile Ltd for 33 months, its ownership of the Boron holding has only lasted
for 10 months (at 1 June 2005) since Boron was acquired on 1 July 2004. Selling the shares in June 2005 will fail the
12 month test, and the gain will become chargeable.
It would be better for the companies to wait for a further month until July 2005 before selling the amalgamated shareholding.
By doing so, they will both be able to take advantage of the substantial shareholdings relief, thereby saving tax of £29,625
assuming a corporation tax rate of 19%.
第3题:
(c) (i) State the date by which Thai Curry Ltd’s self-assessment corporation tax return for the year ended
30 September 2005 should be submitted, and advise the company of the penalties that will be due if
the return is not submitted until 31 May 2007. (3 marks)
(ii) State the date by which Thai Curry Ltd’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005
should be paid, and advise the company of the interest that will be due if the liability is not paid until
31 May 2007. (3 marks)
(c) Self-assessment tax return
(1) Thai Curry Ltd’s self-assessment corporation tax return for the year ended 30 September 2005 must be submitted by
30 September 2006.
(2) If the company does not submit its self-assessment tax return until 31 May 2007, then there will be an automatic fixed
penalty of £200 since the return is more than three months late.
(3) There will also be an additional corporation tax related penalty of £4,415 (44,150 × 10%) being 10% of the tax unpaid,
since the self-assessment tax return is more than six months late.
Corporation tax liability
(1) Thai Curry Ltd’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005 must be paid by 1 July 2006.
(2) If the company does not pay its corporation tax until 31 May 2007, then interest of £3,035 (44,150 at 7·5% = 3,311
× 11/12) will be charged by HM Revenue & Customs for the period 1 July 2006 to 31 May 2007.
第4题:
(c) Calculate the expected corporation tax liability of Dovedale Ltd for the year ending 31 March 2007 on the
assumption that all available reliefs are claimed by Dovedale Ltd but that Hira Ltd will not claim any capital
allowances in that year. (4 marks)


第5题:
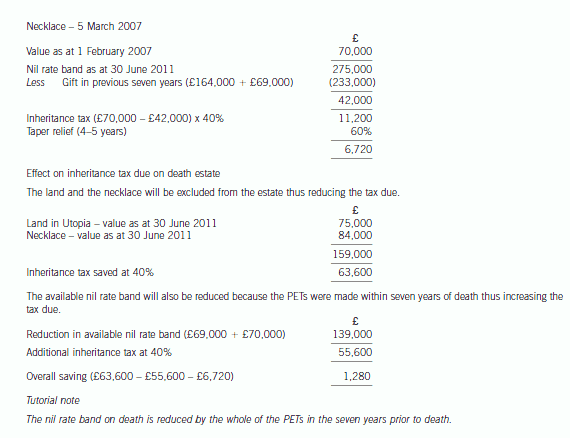
(b) Mabel has two objectives when making the gifts to Bruce and Padma:
(1) To pay no tax on any gift in her lifetime; and
(2) To reduce the eventual liability to inheritance tax on her death.
Advise Mabel which item to gift to Bruce and to Padma in order to satisfy her objectives. Give reasons for
your advice.
Your advice should include a computation of the inheritance tax saved as a result of the two gifts, on the
assumption that Mabel dies on 30 June 2011. (10 marks)

第6题:
(d) Advise on any lifetime inheritance tax (IHT) planning that could be undertaken in respect of both Stuart and
Rebecca to help reduce the potential inheritance tax (IHT) liability calculated in (c) above. (7 marks)
Relevant retail price index figures are:
May 1994 144·7
April 1998 162·6
第7题:
(ii) Explain the income tax (IT), national insurance (NIC) and capital gains tax (CGT) implications arising on
the grant to and exercise by an employee of an option to buy shares in an unapproved share option
scheme and on the subsequent sale of these shares. State clearly how these would apply in Henry’s
case. (8 marks)
第8题:
(c) the deferred tax implications (with suitable calculations) for the company which arise from the recognition
of a remuneration expense for the directors’ share options. (7 marks)

第9题:
(c) Without changing the advice you have given in (b), or varying the terms of Luke’s will, explain how Mabel
could further reduce her eventual inheritance tax liability and quantify the tax saving that could be made.
(3 marks)
The increase in the retail prices index from April 1984 to April 1998 is 84%.
You should assume that the rates and allowances for the tax year 2005/06 will continue to apply for the
foreseeable future.
第10题:
(c) (i) Compute Gloria’s capital gains tax liability for 2006/07 ignoring any claims or elections available to
reduce the liability. (3 marks)
