第1题:
This passage is mainly about ______.
A) the definition of bacteria
B) health germs
C) probiotics
D) probiotics versus antibiotics
第2题:
第3题:
根据抗生素的抗菌范围可将其分为抗()抗生素、抗( )抗生素和( )抗生素。
第4题:
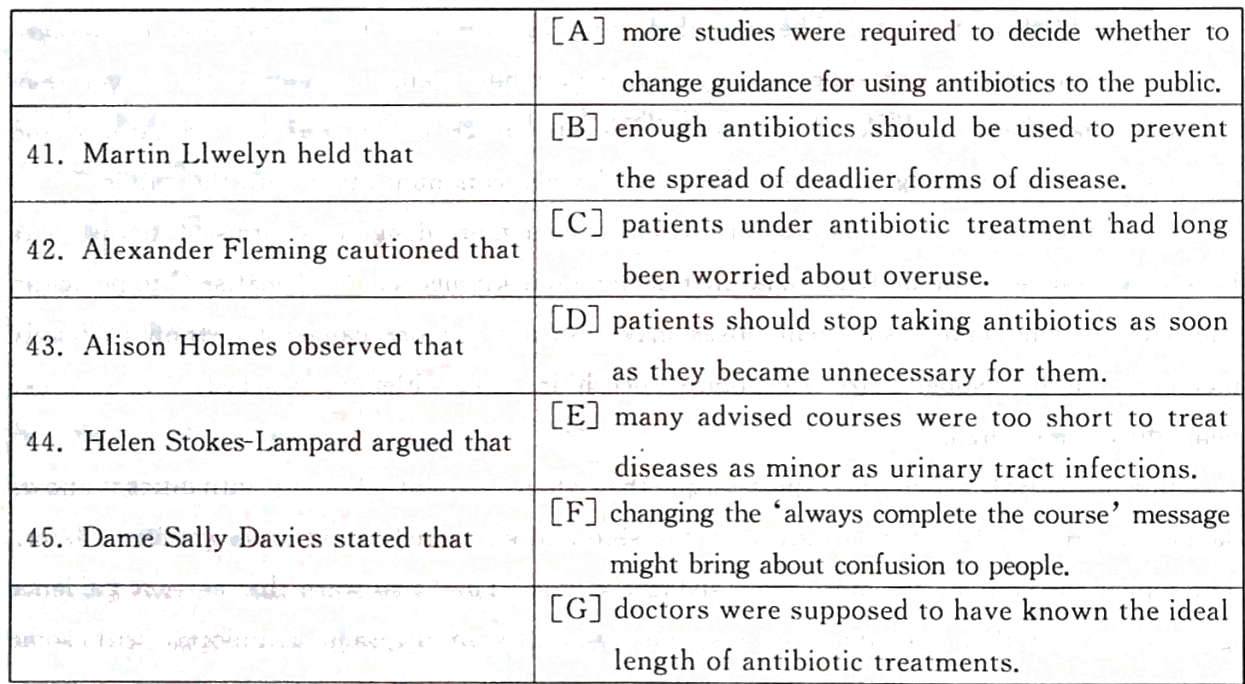
第5题:
第6题:
There is no evidence【 that】 antibiotics, anti-viral medicines or steroids help, so doctors can offer only supportive care.
我知道这是同位语从句,不缺成分,所以【】里用that不用whether,
但我有2个问题:
1.如果一定要用whether的话,这句子该怎么变呢?
2.填whether不对的原因还有什么?感觉whether也很顺口
首先回答楼楼的第二个问题~英语和中文不同,我明白你想表达的意思是“没有证据证明xxxxx是否有效”,但注意,这是我们平时很随意的中文表达,在英文里,这种说法是不存在的。正如楼上朋友所说,There is no evidence/doubt that...这是固定搭配,为什么呢?仔细观察可以发现 no doubt和no evidence都是表达的单项可能性,即它们所传达出的结论只对多种可能性中的一种有效。举个例子吧,一个人被怀疑犯了罪,而他有不在场的证据,这个证据只能证明他没有犯罪,而不能证明他犯了罪,明白了不?所以,这题只能选that,而不能选whether。顺口是固然的,这和我们平时的语言习惯有关,可在逻辑性强而不浪漫的英语环境中这就不对咯!
还有楼楼的第一个问题~
应该可以解决了吧!既然同位语从句只能表达一种可能性,那么定然不能用whether了,所以第一题没有答案。
简单一点来说,There is no evidence/doubt that...就是约定俗成的用法,楼楼不必太钻牛角尖啊!
第7题:
第8题:
It isn't said in the passage that L-GG can be used to ______.
A) lessen symptoms of Crohn's disease
B) fight against rotavirus
C) treat traveler' s diarrhea
D) treat intestinal upsets caused by antibiotics
第9题:
第10题:
抗生素(antibiotics)