A、due
B、owing
C、thanks
D、because
第1题:
b)
main()
{
union{ /*定义一个联合*/
int i;
struct{ /*在联合中定义一个结构*/
char first;
char second;
}half;
}number;
number.i=0x4241; /*联合成员赋值*/
printf("%c%c\n", number.half.first,
mumber.half.second);
number.half.first='a'; /*联合中结构成员赋值
*/
number.half.second='b';
printf("%x\n", number.i);
getch();
}
AB (0x41 对应'A',是低位;Ox42 对应'B',
是高位)6261 (number.i 和number.half 共用一块地址空
间)
第2题:
●试题二
阅读下列函数说明和C代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
该程序运行后,输出下面的数字金字塔

【程序】
include<stdio.h>
main ()
{char max,next;
int i;
for(max=′1′;max<=′9′;max++)
{for(i=1;i<=20- (1) ;++i)
printf(" ");
for(next= (2) ;next<= (3) ;next++)
printf("%c",next);
for(next= (4) ;next>= (5) ;next--)
printf("%c",next);
printf("\n");
}
}
第3题:
When you compare the differences between half-duplex and full-duplex Ethernet, which of the following characteristics are exclusive to half-duplex? (Select two answer choices)
A.Half-duplex Ethernet operates in a shared collision domain.
B.Half-duplex Ethernet operates in an exclusive broadcast domain.
C.Half-duplex Ethernet has efficient throughput.
D.Half-duplex Ethernet has lower effective throughput.
E.Half-duplex Ethernet operates in an exclusive collision domain.
第4题:
在KMP模式匹配中,用next数组存放模式串的部分匹配信息。当模式串位j与目标串位i比较时,两字符不相等,则i的位移方式是()。
A.i=next[j]
B.i不变
C..j不变
D.j=next[j]
第5题:
第6题:
执行下列语句后指针及链表的示意图为(43)。
L = (LinkList) malloc ( sizeof (LNode) );
P = L;
for(i =0;i <=3;i ++) {
P→next = (LinkList) malloc (sizeof (LNode));
P = P→next;
P→data = i * i + 1;
}
A.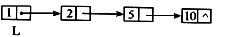
B.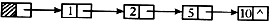
C.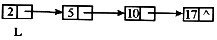
D.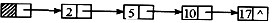
第7题:
A. Half-duplex Ethernet operates in a shared collision domain.
B. Full-duplex Ethernet has a lower effective throughput.
C. Half-duplex Ethernet operates in a private collision domain.
D. Full-duplex Ethernet allows two-way communication.
E. Half-duplex Ethernet operates in a private broadcast domain.
第8题:
#include "stdio.h"void half(void *pval,char type);main(){ int i=20; long l=100000; float ff=12.456; double d=123.044444; printf("%d\n",i); printf("%ld\n",l); printf("%f\n",ff); printf("%lf\n",d); half(&i,'i'); half(&l,'l'); half(&ff,'ff'); half(&d,'d'); printf("\n%d",i); printf("\n%ld",l); printf("\n%f",ff); printf("\n%lf",d); return 0; }void half(void *pval,char type){ switch(type) { case 'i': { *((int *)pval)/=2; //我想问一下,这个语法怎么理解,太复杂了 break; } case 'l': { *((long *)pval)/=2; break; } case 'ff': { *((float *)pval)/=2; break; } case 'd': { *((double *)pval)/=2; break; } } }
第9题:
在KMP模式匹配中,用next数组存放模式串的部分匹配信息。当模式串位j与目标串位i比较时,两字符不相等,则j的位移方式是()。
A.i=next[j]
B.i不变
C.j不变
D.j=next[j]
第10题:
L1是不带头结点的单链表。以下算法功能是什么? Status fun(LinkList &L1, LinkList &L2) {p=L1; n=0; while(p){n++; p=p->next;} p=L1; for(i=1;i<n/2;i++)p=p->next; L2=p->next; p->next=NULL; return OK; }