(b) Ambush loaned $200,000 to Bromwich on 1 December 2003. The effective and stated interest rate for this
loan was 8 per cent. Interest is payable by Bromwich at the end of each year and the loan is repayable on
30 November 2007. At 30 November 2005, the directors of Ambush have heard that Bromwich is in financial
difficulties and is undergoing a financial reorganisation. The directors feel that it is likely that they will only
receive $100,000 on 30 November 2007 and no future interest payment. Interest for the year ended
30 November 2005 had been received. The financial year end of Ambush is 30 November 2005.
Required:
(i) Outline the requirements of IAS 39 as regards the impairment of financial assets. (6 marks)
第1题:
Additionally the directors wish to know how the provision for deferred taxation would be calculated in the following
situations under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’:
(i) On 1 November 2003, the company had granted ten million share options worth $40 million subject to a two
year vesting period. Local tax law allows a tax deduction at the exercise date of the intrinsic value of the options.
The intrinsic value of the ten million share options at 31 October 2004 was $16 million and at 31 October 2005
was $46 million. The increase in the share price in the year to 31 October 2005 could not be foreseen at
31 October 2004. The options were exercised at 31 October 2005. The directors are unsure how to account
for deferred taxation on this transaction for the years ended 31 October 2004 and 31 October 2005.
(ii) Panel is leasing plant under a finance lease over a five year period. The asset was recorded at the present value
of the minimum lease payments of $12 million at the inception of the lease which was 1 November 2004. The
asset is depreciated on a straight line basis over the five years and has no residual value. The annual lease
payments are $3 million payable in arrears on 31 October and the effective interest rate is 8% per annum. The
directors have not leased an asset under a finance lease before and are unsure as to its treatment for deferred
taxation. The company can claim a tax deduction for the annual rental payment as the finance lease does not
qualify for tax relief.
(iii) A wholly owned overseas subsidiary, Pins, a limited liability company, sold goods costing $7 million to Panel on
1 September 2005, and these goods had not been sold by Panel before the year end. Panel had paid $9 million
for these goods. The directors do not understand how this transaction should be dealt with in the financial
statements of the subsidiary and the group for taxation purposes. Pins pays tax locally at 30%.
(iv) Nails, a limited liability company, is a wholly owned subsidiary of Panel, and is a cash generating unit in its own
right. The value of the property, plant and equipment of Nails at 31 October 2005 was $6 million and purchased
goodwill was $1 million before any impairment loss. The company had no other assets or liabilities. An
impairment loss of $1·8 million had occurred at 31 October 2005. The tax base of the property, plant and
equipment of Nails was $4 million as at 31 October 2005. The directors wish to know how the impairment loss
will affect the deferred tax provision for the year. Impairment losses are not an allowable expense for taxation
purposes.
Assume a tax rate of 30%.
Required:
(b) Discuss, with suitable computations, how the situations (i) to (iv) above will impact on the accounting for
deferred tax under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’ in the group financial statements of Panel. (16 marks)
(The situations in (i) to (iv) above carry equal marks)
(b) (i) The tax deduction is based on the option’s intrinsic value which is the difference between the market price and exercise
price of the share option. It is likely that a deferred tax asset will arise which represents the difference between the tax
base of the employee’s service received to date and the carrying amount which will effectively normally be zero.
The recognition of the deferred tax asset should be dealt with on the following basis:
(a) if the estimated or actual tax deduction is less than or equal to the cumulative recognised expense then the
associated tax benefits are recognised in the income statement
(b) if the estimated or actual tax deduction exceeds the cumulative recognised compensation expense then the excess
tax benefits are recognised directly in a separate component of equity.
As regards the tax effects of the share options, in the year to 31 October 2004, the tax effect of the remuneration expensewill be in excess of the tax benefit.
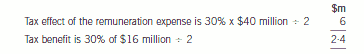
The company will have to estimate the amount of the tax benefit as it is based on the share price at 31 October 2005.
The information available at 31 October 2004 indicates a tax benefit based on an intrinsic value of $16 million.
As a result, the tax benefit of $2·4 million will be recognised within the deferred tax provision. At 31 October 2005,
the options have been exercised. Tax receivable will be 30% x $46 million i.e. $13·8 million. The deferred tax asset
of $2·4 million is no longer recognised as the tax benefit has crystallised at the date when the options were exercised.
For a tax benefit to be recognised in the year to 31 October 2004, the provisions of IAS12 should be complied with as
regards the recognition of a deferred tax asset.
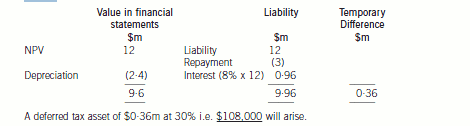
(ii) Plant acquired under a finance lease will be recorded as property, plant and equipment and a corresponding liability for
the obligation to pay future rentals. Rents payable are apportioned between the finance charge and a reduction of the
outstanding obligation. A temporary difference will effectively arise between the value of the plant for accounting
purposes and the equivalent of the outstanding obligation as the annual rental payments qualify for tax relief. The tax
base of the asset is the amount deductible for tax in future which is zero. The tax base of the liability is the carrying
amount less any future tax deductible amounts which will give a tax base of zero. Thus the net temporary differencewill be:
(iii) The subsidiary, Pins, has made a profit of $2 million on the transaction with Panel. These goods are held in inventory
at the year end and a consolidation adjustment of an equivalent amount will be made against profit and inventory. Pins
will have provided for the tax on this profit as part of its current tax liability. This tax will need to be eliminated at the
group level and this will be done by recognising a deferred tax asset of $2 million x 30%, i.e. $600,000. Thus any
consolidation adjustments that have the effect of deferring or accelerating tax when viewed from a group perspective will
be accounted for as part of the deferred tax provision. Group profit will be different to the sum of the profits of the
individual group companies. Tax is normally payable on the profits of the individual companies. Thus there is a need
to account for this temporary difference. IAS12 does not specifically address the issue of which tax rate should be used
calculate the deferred tax provision. IAS12 does generally say that regard should be had to the expected recovery or
settlement of the tax. This would be generally consistent with using the rate applicable to the transferee company (Panel)
rather than the transferor (Pins).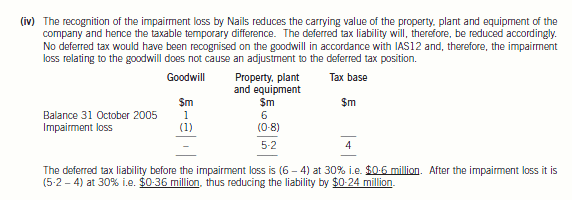
第2题:
(ii) Explain the accounting treatment under IAS39 of the loan to Bromwich in the financial statements of
Ambush for the year ended 30 November 2005. (4 marks)
第3题:
23 The capital structure of a company at 30 June 2005 is as follows:
$m
Ordinary share capital 100
Share premium account 40
Retained earnings 60
10% Loan notes 40
The company’s income statement for the year ended 30 June 2005 showed:
$m
Operating profit 44
Loan note interest (4)
___
Profit for year 40
____
What is the company’s return on capital employed?
A 40/240 = 162/3 per cent
B 40/100 = 40 per cent
C 44/240 = 181/3 per cent
D 44/200 = 22 per cent
第4题:
(d) The management of Wonderland plc have become concerned about the increased level of operating costs
associated with its petrol-driven ferries and have made a strategic decision to dispose of these. They are now
considering entering into a contract with the Newman Steamship Company (NSC), a shipping organisation based
in Robynland. The contract would entail NSC providing transport to and from Cinola Island for all visitors to the
zoo and circus.
As a result of negotiations with NSC, the directors of Wonderland plc are considering two options whereby NSC
will become responsible for the transportation of visitors to and from Cinola Island with effect from 1 December
2007 or 1 December 2008.
Additional information is available as follows:
(1) NSC would require Wonderland plc to pay for the necessary modifications to their steamships in order that
they would satisfy marine regulations with regard to passenger transportation. The only firm which could
undertake this work is currently working to full capacity and would require a payment of £2,450,000 in
order to undertake the work necessary so that the ferries could be in operation by 1 December 2007. The
same firm would require a payment of £1,725,000 in order to make the necessary modifications so that
the ferries could be in operation by 1 December 2008. The government of Robynland would be willing to
pay a grant of 8% towards the cost of getting the ferries into operation by 1 December 2007, but would not
be willing to pay a grant in respect of any later date.
(2) On 1 December 2002 Wonderland plc paid £500,000 to the Port Licencing Authority of Robynland. This
payment was for a licence which entitles Wonderland plc to use all harbour facilities in Robynland during
the five-year period ending 30 November 2007. The licence could be renewed on 1 December 2007 at a
cost of £150,000 per annum.
(3) Redundancy payments would need to be paid in respect of loss of employment. These would amount to
£1,200,000 if the contract with NSC commenced on 1 December 2007. This amount would reduce to
£750,000 if the contract commenced on 1 December 2008.
(4) Wonderland plc has a contract for the provision of petrol for its ferries which is due to expire on 30 November
2008. Early termination of the contract would incur a penalty charge of £76,000. An emergency reserve
stock of petrol held by Wonderland plc, which cannot be used after 30 November 2007 due to marine
regulations regarding the age of fuel, could be sold for £55,000 on 1 December 2007 but not on any date
thereafter.
(5) The ferries could be sold for £3,300,000 on 1 December 2007. If retained after 1 December 2007 the
ferries would require servicing during the year ending 30 November 2008 which would incur costs
amounting to £150,000. The resale value of the ferries on 1 December 2008 would be £2,900,000.
(6) Stock of consumable items which originally cost £150,000 could be sold on 1 December 2007 for
£110,000 and on 1 December 2008 for £50,000.
Required:
(i) On purely financial grounds, advise whether the management of Wonderland plc should enter into a
contract with NSC with effect from 1 December 2007 or 1 December 2008. You may ignore the time
value of money. (9 marks)
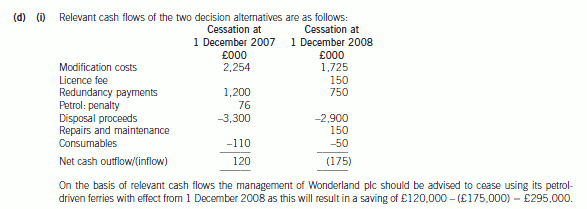
第5题:
(d) Sirus raised a loan with a bank of $2 million on 1 May 2007. The market interest rate of 8% per annum is to
be paid annually in arrears and the principal is to be repaid in 10 years time. The terms of the loan allow Sirus
to redeem the loan after seven years by paying the full amount of the interest to be charged over the ten year
period, plus a penalty of $200,000 and the principal of $2 million. The effective interest rate of the repayment
option is 9·1%. The directors of Sirus are currently restructuring the funding of the company and are in initial
discussions with the bank about the possibility of repaying the loan within the next financial year. Sirus is
uncertain about the accounting treatment for the current loan agreement and whether the loan can be shown as
a current liability because of the discussions with the bank. (6 marks)
Appropriateness of the format and presentation of the report and quality of discussion (2 marks)
Required:
Draft a report to the directors of Sirus which discusses the principles and nature of the accounting treatment of
the above elements under International Financial Reporting Standards in the financial statements for the year
ended 30 April 2008.
第6题:
4 Ryder, a public limited company, is reviewing certain events which have occurred since its year end of 31 October
2005. The financial statements were authorised on 12 December 2005. The following events are relevant to the
financial statements for the year ended 31 October 2005:
(i) Ryder has a good record of ordinary dividend payments and has adopted a recent strategy of increasing its
dividend per share annually. For the last three years the dividend per share has increased by 5% per annum.
On 20 November 2005, the board of directors proposed a dividend of 10c per share for the year ended
31 October 2005. The shareholders are expected to approve it at a meeting on 10 January 2006, and a
dividend amount of $20 million will be paid on 20 February 2006 having been provided for in the financial
statements at 31 October 2005. The directors feel that a provision should be made because a ‘valid expectation’
has been created through the company’s dividend record. (3 marks)
(ii) Ryder disposed of a wholly owned subsidiary, Krup, a public limited company, on 10 December 2005 and made
a loss of $9 million on the transaction in the group financial statements. As at 31 October 2005, Ryder had no
intention of selling the subsidiary which was material to the group. The directors of Ryder have stated that there
were no significant events which have occurred since 31 October 2005 which could have resulted in a reduction
in the value of Krup. The carrying value of the net assets and purchased goodwill of Krup at 31 October 2005
were $20 million and $12 million respectively. Krup had made a loss of $2 million in the period 1 November
2005 to 10 December 2005. (5 marks)
(iii) Ryder acquired a wholly owned subsidiary, Metalic, a public limited company, on 21 January 2004. The
consideration payable in respect of the acquisition of Metalic was 2 million ordinary shares of $1 of Ryder plus
a further 300,000 ordinary shares if the profit of Metalic exceeded $6 million for the year ended 31 October
2005. The profit for the year of Metalic was $7 million and the ordinary shares were issued on 12 November
2005. The annual profits of Metalic had averaged $7 million over the last few years and, therefore, Ryder had
included an estimate of the contingent consideration in the cost of the acquisition at 21 January 2004. The fair
value used for the ordinary shares of Ryder at this date including the contingent consideration was $10 per share.
The fair value of the ordinary shares on 12 November 2005 was $11 per share. Ryder also made a one for four
bonus issue on 13 November 2005 which was applicable to the contingent shares issued. The directors are
unsure of the impact of the above on earnings per share and the accounting for the acquisition. (7 marks)
(iv) The company acquired a property on 1 November 2004 which it intended to sell. The property was obtained
as a result of a default on a loan agreement by a third party and was valued at $20 million on that date for
accounting purposes which exactly offset the defaulted loan. The property is in a state of disrepair and Ryder
intends to complete the repairs before it sells the property. The repairs were completed on 30 November 2005.
The property was sold after costs for $27 million on 9 December 2005. The property was classified as ‘held for
sale’ at the year end under IFRS5 ‘Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’ but shown at
the net sale proceeds of $27 million. Property is depreciated at 5% per annum on the straight-line basis and no
depreciation has been charged in the year. (5 marks)
(v) The company granted share appreciation rights (SARs) to its employees on 1 November 2003 based on ten
million shares. The SARs provide employees at the date the rights are exercised with the right to receive cash
equal to the appreciation in the company’s share price since the grant date. The rights vested on 31 October
2005 and payment was made on schedule on 1 December 2005. The fair value of the SARs per share at
31 October 2004 was $6, at 31 October 2005 was $8 and at 1 December 2005 was $9. The company has
recognised a liability for the SARs as at 31 October 2004 based upon IFRS2 ‘Share-based Payment’ but the
liability was stated at the same amount at 31 October 2005. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatment of the above events in the financial statements of the Ryder Group for the year
ended 31 October 2005, taking into account the implications of events occurring after the balance sheet date.
(The mark allocations are set out after each paragraph above.)
(25 marks)
第7题:
(c) Issue of bond
The club proposes to issue a 7% bond with a face value of $50 million on 1 January 2007 at a discount of 5%
that will be secured on income from future ticket sales and corporate hospitality receipts, which are approximately
$20 million per annum. Under the agreement the club cannot use the first $6 million received from corporate
hospitality sales and reserved tickets (season tickets) as this will be used to repay the bond. The money from the
bond will be used to pay for ground improvements and to pay the wages of players.
The bond will be repayable, both capital and interest, over 15 years with the first payment of $6 million due on
31 December 2007. It has an effective interest rate of 7·7%. There will be no active market for the bond and
the company does not wish to use valuation models to value the bond. (6 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above proposals would be dealt with in the financial statements of Seejoy for the year ending
31 December 2007, setting out their accounting treatment and appropriateness in helping the football club’s
cash flow problems.
(Candidates do not need knowledge of the football finance sector to answer this question.)
(c) Issue of bond
This form. of financing a football club’s operations is known as ‘securitisation’. Often in these cases a special purpose vehicle
is set up to administer the income stream or assets involved. In this case, a special purpose vehicle has not been set up. The
benefit of securitisation of the future corporate hospitality sales and season ticket receipts is that there will be a capital
injection into the club and it is likely that the effective interest rate is lower because of the security provided by the income
from the receipts. The main problem with the planned raising of capital is the way in which the money is to be used. The
use of the bond for ground improvements can be commended as long term cash should be used for long term investment but
using the bond for players’ wages will cause liquidity problems for the club.
This type of securitisation is often called a ‘future flow’ securitisation. There is no existing asset transferred to a special purpose
vehicle in this type of transaction and, therefore, there is no off balance sheet effect. The bond is shown as a long term liability
and is accounted for under IAS39 ‘Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement’. There are no issues of
derecognition of assets as there can be in other securitisation transactions. In some jurisdictions there are legal issues in
assigning future receivables as they constitute an unidentifiable debt which does not exist at present and because of this
uncertainty often the bond holders will require additional security such as a charge on the football stadium.
The bond will be a financial liability and it will be classified in one of two ways:
(i) Financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss include financial liabilities that the entity either has incurred for
trading purposes and, where permitted, has designated to the category at inception. Derivative liabilities are always
treated as held for trading unless they are designated and effective as hedging instruments. An example of a liability held
for trading is an issued debt instrument that the entity intends to repurchase in the near term to make a gain from shortterm
movements in interest rates. It is unlikely that the bond will be classified in this category.
(ii) The second category is financial liabilities measured at amortised cost. It is the default category for financial liabilities
that do not meet the criteria for financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss. In most entities, most financial
liabilities will fall into this category. Examples of financial liabilities that generally would be classified in this category are
account payables, note payables, issued debt instruments, and deposits from customers. Thus the bond is likely to be
classified under this heading. When a financial liability is recognised initially in the balance sheet, the liability is
measured at fair value. Fair value is the amount for which a liability can be settled between knowledgeable, willing
parties in an arm’s length transaction. Since fair value is a market transaction price, on initial recognition fair value will
usually equal the amount of consideration received for the financial liability. Subsequent to initial recognition financial
liabilities are measured using amortised cost or fair value. In this case the company does not wish to use valuation
models nor is there an active market for the bond and, therefore, amortised cost will be used to measure the bond.
The bond will be shown initially at $50 million × 95%, i.e. $47·5 million as this is the consideration received. Subsequentlyat 31 December 2007, the bond will be shown as follows:

第8题:
(c) (i) State the date by which Thai Curry Ltd’s self-assessment corporation tax return for the year ended
30 September 2005 should be submitted, and advise the company of the penalties that will be due if
the return is not submitted until 31 May 2007. (3 marks)
(ii) State the date by which Thai Curry Ltd’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005
should be paid, and advise the company of the interest that will be due if the liability is not paid until
31 May 2007. (3 marks)
(c) Self-assessment tax return
(1) Thai Curry Ltd’s self-assessment corporation tax return for the year ended 30 September 2005 must be submitted by
30 September 2006.
(2) If the company does not submit its self-assessment tax return until 31 May 2007, then there will be an automatic fixed
penalty of £200 since the return is more than three months late.
(3) There will also be an additional corporation tax related penalty of £4,415 (44,150 × 10%) being 10% of the tax unpaid,
since the self-assessment tax return is more than six months late.
Corporation tax liability
(1) Thai Curry Ltd’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005 must be paid by 1 July 2006.
(2) If the company does not pay its corporation tax until 31 May 2007, then interest of £3,035 (44,150 at 7·5% = 3,311
× 11/12) will be charged by HM Revenue & Customs for the period 1 July 2006 to 31 May 2007.
第9题:
(b) Calculate the percentage of maximum capacity at which the zoo will break even during the year ending
30 November 2007. You should assume that 50% of the revenue from sales of ticket type ZC is attributable
to the zoo. (7 marks)

第10题:
(ii) Describe the procedures to verify the number of serious accidents in the year ended 30 November 2007.
(4 marks)